Describe the Events That Make Up the Cardiac Cycle
Pressure is building in ventricles. The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole.

Cardiac Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ii Beginning of Ventricular Systole The contraction of ventricles begin due to the wave of.
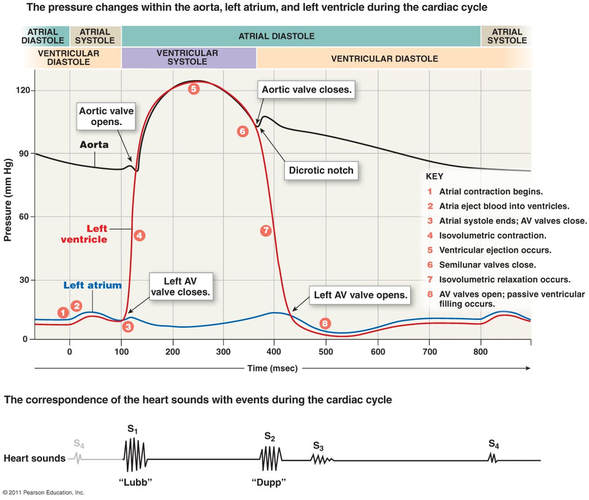
. Start studying describe the events of a cardiac cycle. Isovolumetric contraction Rapid ejection Reduced ejection 4Ventricular diastole Proto diastole Isovolumetric ventricular relaxation Earlier rapid filling Reduced filling Last rapid filling due to atrial systole Atrial systole. The cardiac cycle describes all the activities of the heart through one complete heartbeatthat is through one contraction and relaxation of both the atria and ventricles.
The cycle begins with the SAN sino-atrial node. Period of ventricular contraction and blood ejection 2 Diastole. The cardiac cycle attributes to a comprehensive heartbeat from its production to the commencement of the next beat.
Traveling down where it reaches the purkinje fibres then the myocardial cells that make up the ventricles 4 Spontaneous Discharge Rates of the heart nodes. The heart is equipped with four chambers and one-way valves that work with precision to pump blood to and from the body. At this stage semilunar valves are closed.
Lub heard in this phase Ventricular ejection phase Pressure rises even more. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. The successive events of the cardiac cycle are briefly described as below.
The period of time that begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle. Pulmonary and Aortic valves open. The inlet valve is open and the outlet valve is closed.
Describe the events of the cardiac cycle. The contraction of the heart muscles called systole and the relaxation period known as diastole. Most but not all blood ejects out of ventricles.
The aortic and pulmonary valves are not yet open however and so no ejection occurs during this isovolumetric ventricular contraction. It consists of two parts. Beginning with all chambers in diastole blood flows passively from the veins into the atria and past the atrioventricular valves into the ventricles.
Atria Ventricles Valves Ventricular filling Isovolumetric contraction Ventricular ejection Isovolumetric relaxation Ventricular filling again. This is the hearts pacemaker. Describe the cardiac cycle atrial systole.
In the diastole phase heart ventricles relax and the heart fills with blood. The shortest phase of the cardiac cycle. Cardiac cycle phases Atrial diastole.
Explain the status of the atria ventricles and heart valves during the following phases of the cardiac cycle. The cardiac cycle comprises a complete relaxation and contraction of both the atria and ventricles and lasts approximately 08 seconds. At the beginning of a cardiac cycle all the four chambers of heart is in diastole.
At the onset of systole ventricular pressure rapidly exceeds atrial pressure and the AV valves close. The autonomous sinuatrial node initiates an action potential that is propagated. It is how the heart operates and what exactly happens when it contracts and relaxes.
Atrial diastole is the very first event of the cardiac cycle. The diastole phase and the systole phase. There are two phases of the cardiac cycle.
The sequential events in a heart-beat comprise the cardiac cycle. Increased atrial pressure tricuspid and mitral valves are open ventricular filling occurs ventricular systole. Describe the rates of impulses that travel during a cardiac impulse.
As the heart beats it circulates blood through pulmonary and systemic circuits of the body. When the tricuspid and bicuspid valves open blood from pulmonary veins and vena cava flows respectively Into the left and right auricles. Generally the cardiac cycle can be divided into two separate periods.
A contraction event of either the atria or ventricles is referred to as systole. The cardiac cycle is divided into systole ventricular contraction and diastole ventricular relaxation. The sequence of electrical and mechanical events occurring in the heart during a single beat.
Four phases of the cardiac cycle. Each part of the cardiac cycle consists of several phases characterized by either. The cardiac cycle is a period from the beginning of one heart beat to the beginning of the next one.
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats. Between the left ventricle and aorta. Isovolumetric ventricular contraction all valves closed increased ventricular pressure pulmonary and aortic valves open ventricular emptying and atrial filling occur.
Mechanical events of the cardiac cycle 1Atrial systole 2Atrial diastole 3Ventricular systole. These events result in changes in pressure flow and volume in the various cardiac chambers. Ventricular relaxation called.
Study Electrical Events of the Cardiac Cycle flashcards from Seif Alshunnars class online. Ventricular contraction called. No valves are open.
It sends out a nerve impulse which spreads over the atria and causes them to contract atria systole forcing blood into the ventricals. The blood is forced into the ventricles as the bicuspid valves are open. Following events take place in a cardiac cycle.
I Atrial Systole The atria contract due to the wave of contraction stimulated by the SA node. Consists of 2 phases. The cardiac cycle is the series of events that leads to blood being pumped to the lungs and around the body.
Systole and diastole occur through a series of events marked by structural changes of the cardiac chambers the atria and ventricles. It comprises diastole the systole and the intervening pause. It occurs some milliseconds before the.
The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole. Period of ventricular relaxation and filling. The Cardiac Cycle The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occur in the heart during one heart beat.
The occurrence of a cardiac cycle is illustrated by a heart rate which is naturally indicated as beats per minute.

The Cardiac Cycle Biology For Majors Ii

The Cardiac Cycle Biology For Majors Ii

D4 Function Of The Heart Core Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Chapter 19 Cardiac Cycle Physiology Flashcards Quizlet
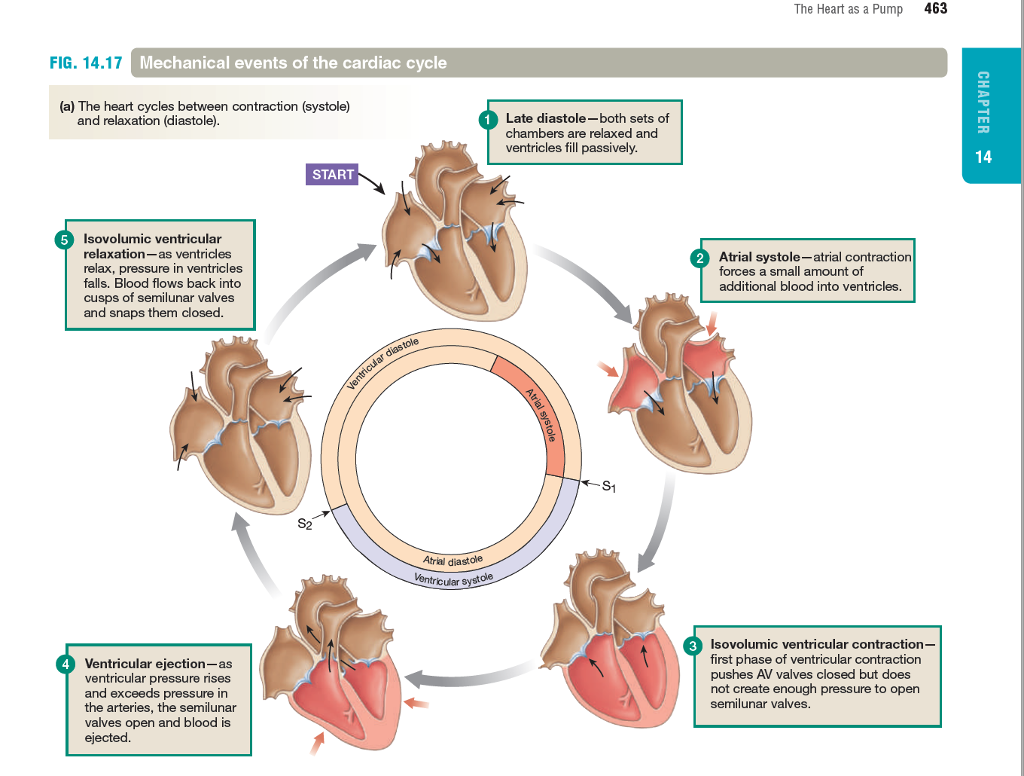
Solved Cardiac Cycle Can You Walk Your Way Through The Chegg Com
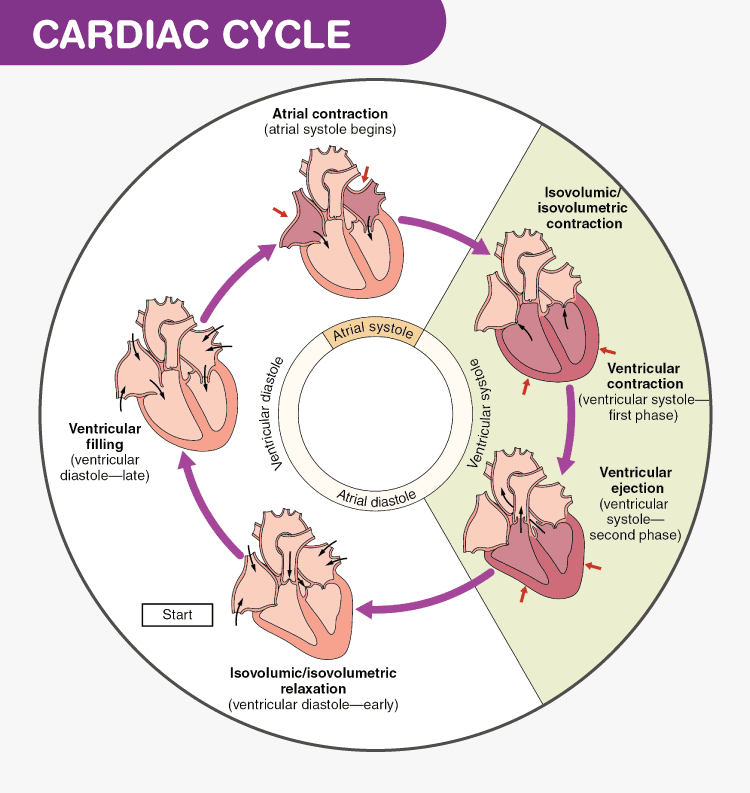
Cardiac Cycle Physiology Diagram Phases Of The Cardiac Cycle

The Blood Flow Through The Heart During The Cardiac Cycle In Download Scientific Diagram

The Cardiac Cycle Demystified Youtube

Cardiac Cycle And Heart Sound Online Biology Notes

Cardiac Cycle Definition Phases And Heart Sounds
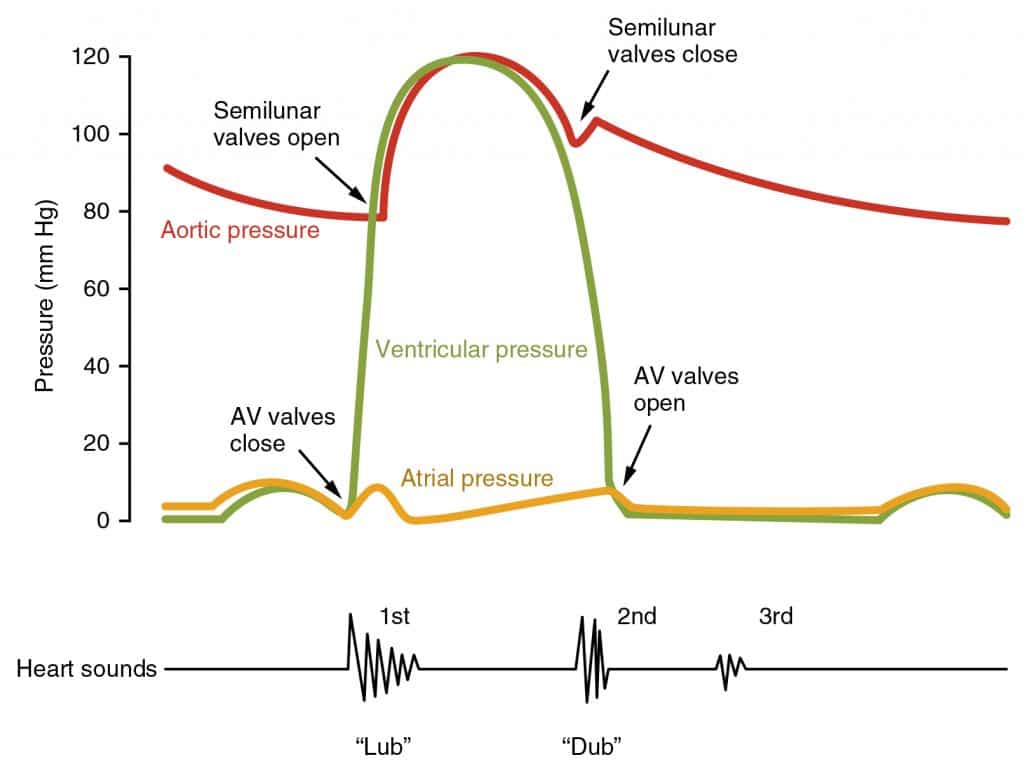
The Cardiac Cycle Pressures In The Heart Teachmephysiology
Events Of Cardiac Cycle And Cardiac Output
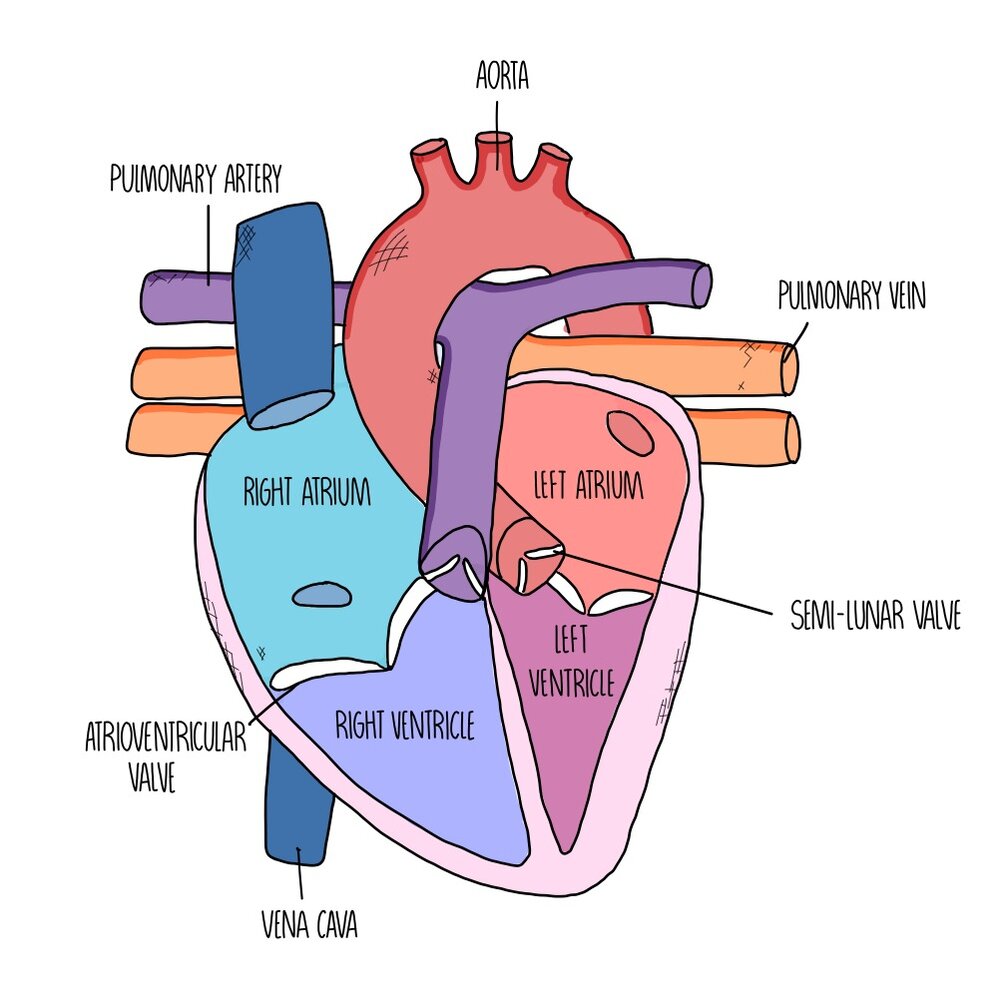
Heart Structure And Cardiac Cycle A Level The Science Hive

19 3 Cardiac Cycle Anatomy Physiology

19 3 Cardiac Cycle Anatomy Physiology

The Cardiac Cycle And Ecg Segments Download Scientific Diagram



Comments
Post a Comment